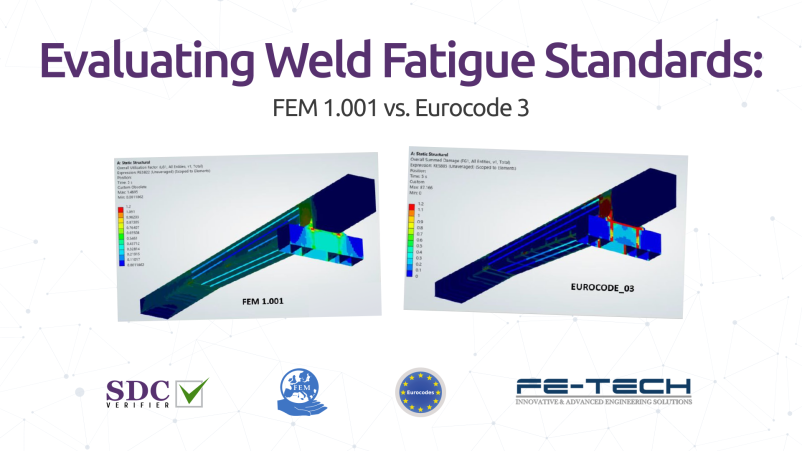
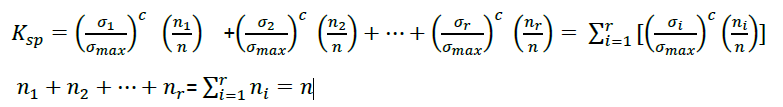Comparing Weld Fatigue Standards: FEM 1.001 vs. Eurocode 3 Using SDC Verifier

Weld fatigue plays a critical role in the structural integrity of cranes and general steel structures. Selecting the appropriate fatigue assessment standard directly impacts design safety, operational efficiency, and compliance. FEM 1.001 and Eurocode 3 are two commonly applied fatigue standards, each with a distinct methodology for evaluating weld strength and fatigue resistance.
FE-Tech conducted a study using structural design and analysis software SDC Verifier to compare FEM 1.001 and Eurocode 3 in assessing weld fatigue. This article presents a detailed breakdown of the study, explaining how each standard approaches fatigue evaluation and what engineers need to consider when selecting between them.
FEM 1.001
Stress Fatigue depends on:
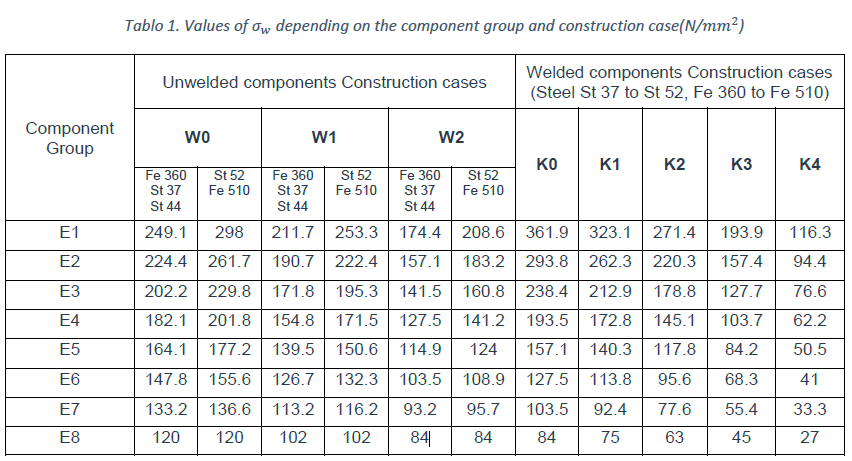
- Weld Type (W0-W2, K0-K4);
- Element Group / Loading Group (E1-E8);
- Material Type ( St360/St37, St510/St52).
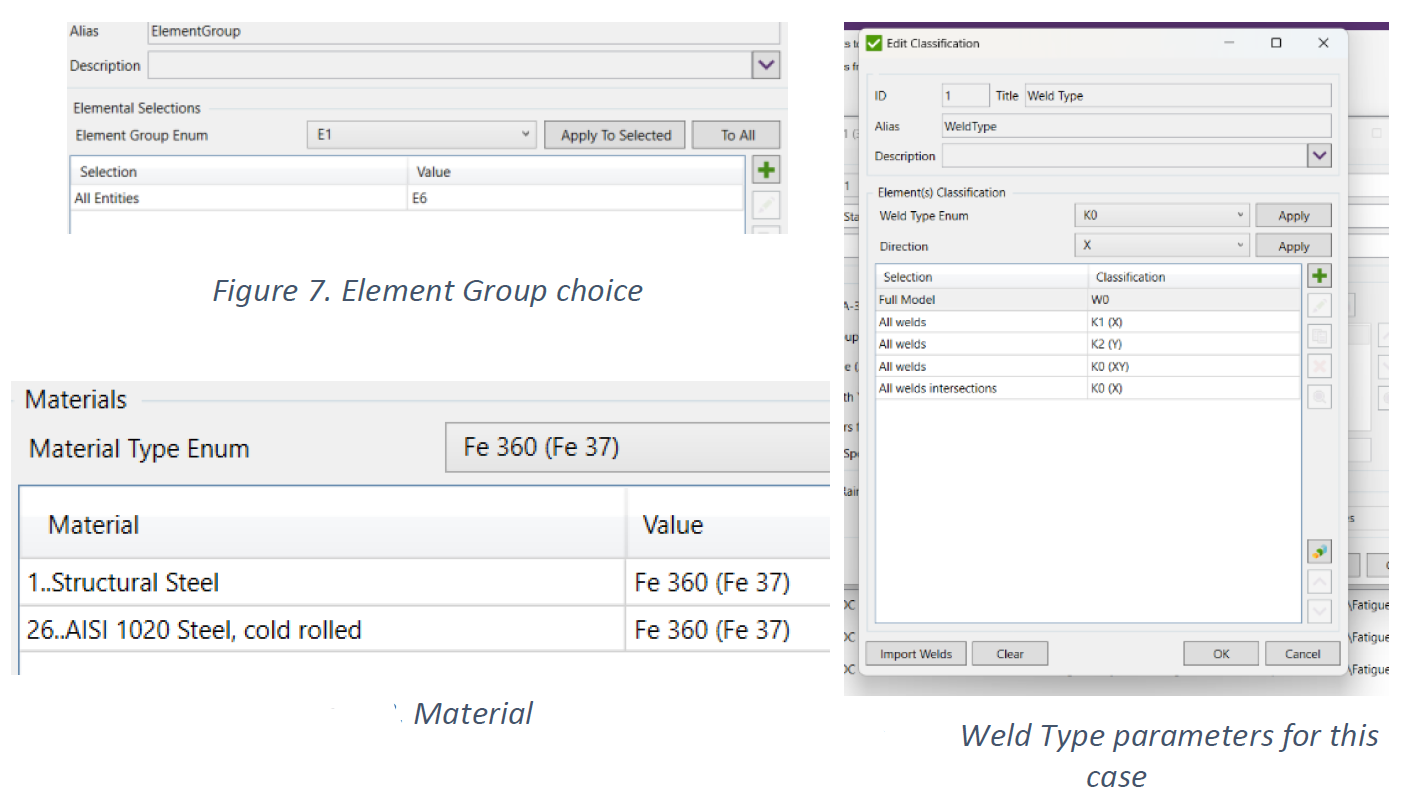
How to select weld type in SDC Verifier?
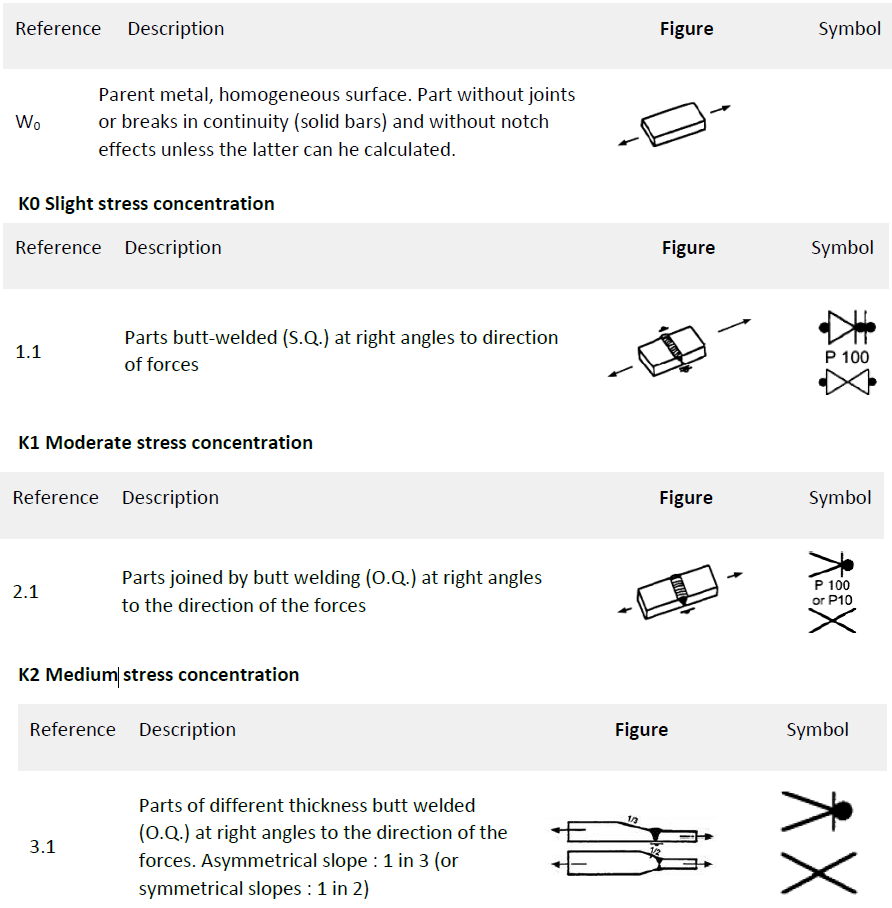
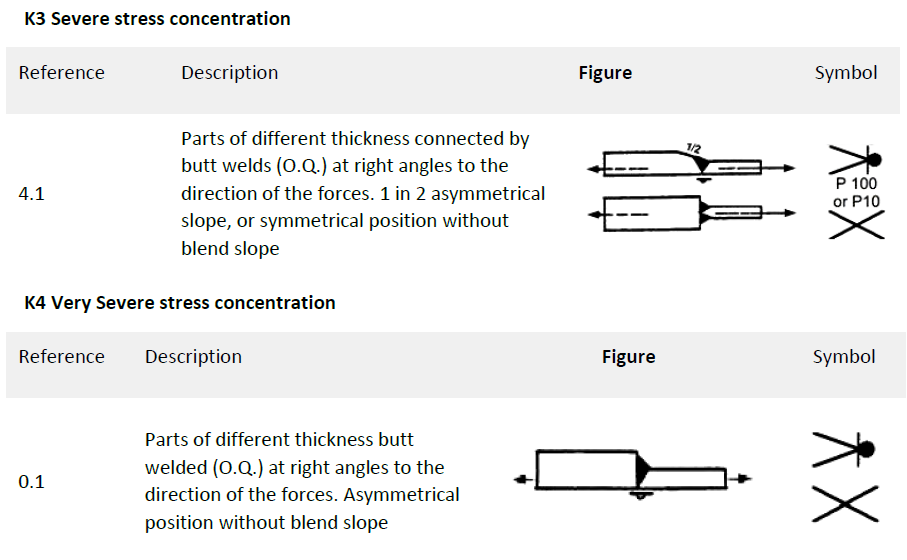
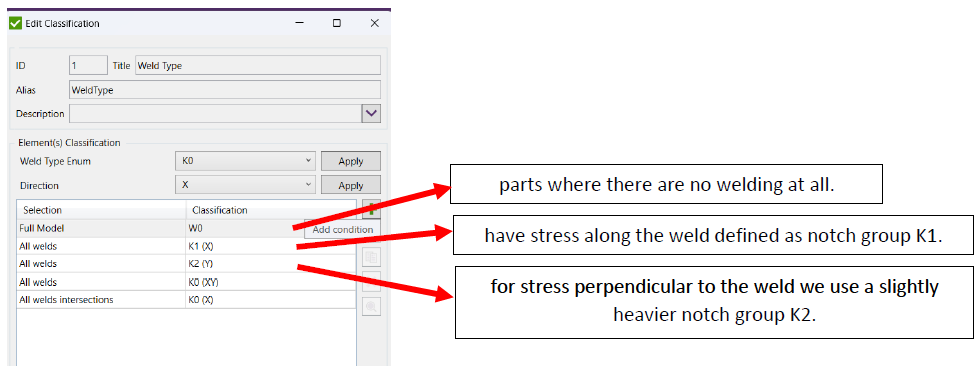
Weld Type – also called Notch Case, defines which elements belong to what weld type (K0-K4 – joints affected by welding, W0-W2 – elements and joints, not affected by welding). Weld Type depends on shape, structural design, whole pattern or type and quality of welds.
While 𝜎𝑤 is the allowable stress limit and κ is th stress ratio (Kappa Factor).
To determine 𝜎𝑤, you can use two approaches:
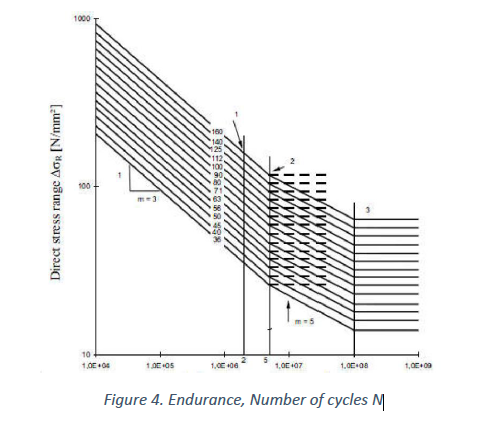
1. Using the MJK Diagram (Graphical Approach)
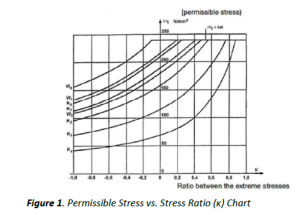
The diagram on the right side provides permissible stress values as a function of the ratio between extreme stresses κ. The steps are:
Identify the given κ value (x-axis).
- Locate the corresponding curve based on the material type and construction case (e.g., W0, W1, K0, etc.).
- Read the permissible stress 𝜎𝑡 from the y-axis.
- Use the relationship between 𝜎𝑡 and 𝜎𝑤 to compute 𝜎𝑤 if needed.
2. Using Equations (Analytical Approach)
a) κ ≤ 0
- For tension: 𝜎𝑡 = 5 . 𝜎𝑤 / (3 – 2 . κ)
- For compression: 𝜎𝑐=2 . 𝜎𝑤/(1- κ)
b) κ > 0
- For tension: 𝜎𝑡 = 𝜎0/[1- κ . (1 – 𝜎0/𝜎+1)]
- For compression: 𝜎𝑐 = 1.2 . 𝜎𝑡
𝝈𝟎=1.66 . 𝝈𝒘(for κ = 0).
𝝈+𝟏=0.75 . 𝜎𝑅 (for κ = +1).
𝝈𝑹 ultimate strength.
𝜎𝑡 is limited in every case to 0.75 . 𝜎𝑅.
By way of illustration, Figure 1. shows curves giving the permissible stress as a function of the ratio κ for the following cases:
- steel A.52;
- predominant tensile stress;
- group E6;
- construction cases W0, W1, W2 for unwelded components and cases of construction for joints K0 to K4.
The permissible stresses have been limited to 240 N/mm², to the permissible stress adopted for checking ultimate strength.
Utilization Factor Combined (calculated stresses devided by the allowable stress)
(𝜎𝑥 𝑚𝑎𝑥/ 𝜎𝑥𝑎)2 + (𝜎𝑦 𝑚𝑎𝑥 / 𝜎𝑦𝑎 )2 – 𝜎𝑥 𝑚𝑎𝑥 .𝜎𝑦 𝑚𝑎𝑥 / (| 𝜎𝑥𝑎 | . | 𝜎𝑦𝑎 |) + (𝜏𝑥𝑦 𝑚𝑎𝑥/𝜏𝑥𝑦𝑎 )2 ≤ 1
where the stress values 𝜎𝑥𝑎, 𝜎𝑦𝑎 and 𝜏𝑥𝑦𝑎 are those resulting from the application of formulae (1), (2), (3) and (4) limited to 0.75 ⋅ 𝜎𝑅
Stress Fatigue is used in Fatigue Allowable Stress calculations.
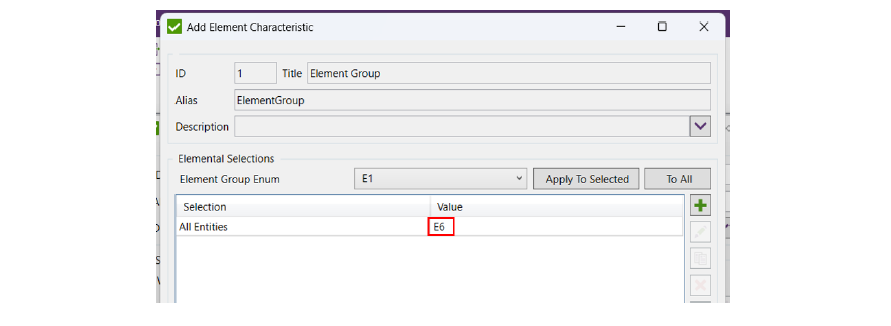
How to select element group in SDC Verifier?
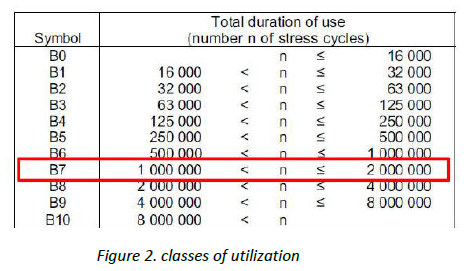
Need to select load spectrum, which means according to the standard, the structure is repeatedly loaded with the work load but the average load is between A and B of the working load, by selecting a load spectrum of 𝑃𝑖.
| Symbol | Spectrum Factor (𝑘𝑠𝑝) |
|---|---|
| P1 | 𝑘𝑠𝑝 ≤ 0.125 |
| P2 | 0.125 < 𝑘𝑠𝑝 ≤ 0.250 |
| P3 | 0.250 < 𝑘𝑠𝑝 ≤ 0.500 |
| P4 | 0.500 < 𝑘𝑠𝑝 ≤ 1.000 |
| Load Spectrum | Remarks |
| P0 | Very light | P=0 | Crane by exception loaded with the working load, and as a rule, with very light loads |
| P1 | Light | P=1/3 | Crane sometimes loaded with the working load, and as a rule with loads of about 1/3 of the working load |
| P2 | Moderate | P=2/3 | Crane repeatedly loaded with the working load, and as a rule with loads between 1/3 and 2/3 of the working load |
| P3 | Heavy | P=1 | Crane frequently loaded with the working load |
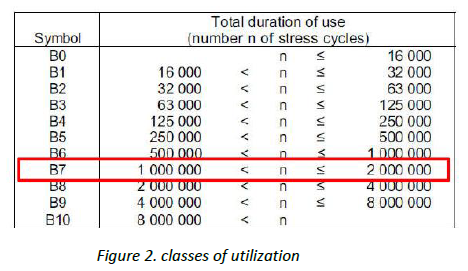
And maximum number of load cases of B, Class of Utilization B7 (1.8 million < 2 x 106).
which gives utilization class E we end up with element group of 𝐸𝑖.
We need to select the type of welding or notch group, and in our model we keep it simple out of 7 possible classifications we only use 3 of them, we have parts where there are no welding at all, which is W0 which is the best category, and have stress along the weld defined as notch group K1, and for stress perpendicular to the weld we use a slightly heavier notch group K2.
Eurocode 03
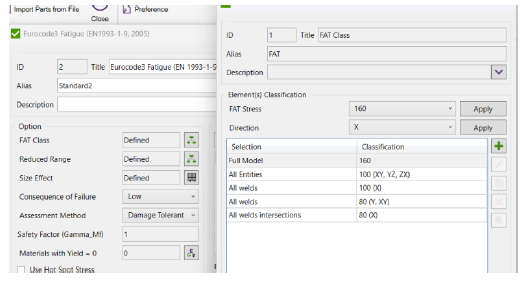
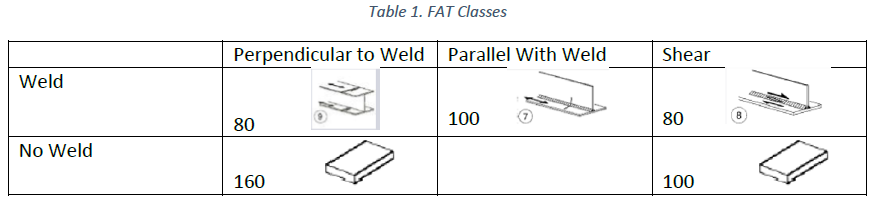
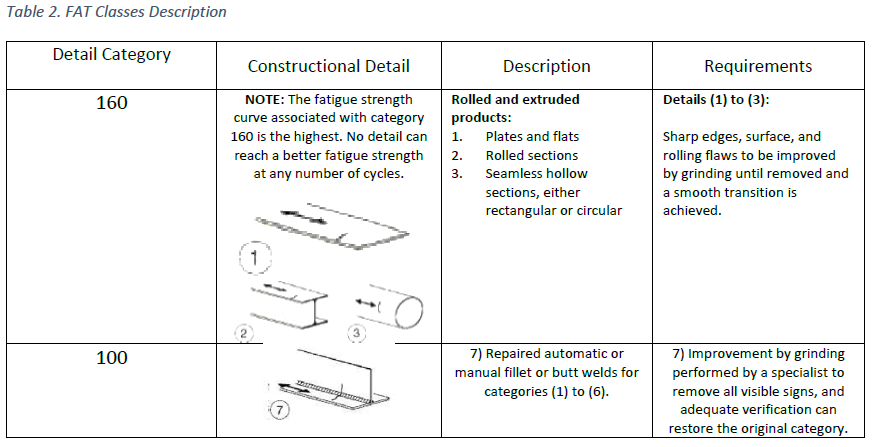
FAT Class – the fatigue strength for nominal stress ranges is represented by a series of (𝑙𝑜𝑔Δ𝜎𝑅)-(𝑙𝑜𝑔 𝑁) curves and (𝑙𝑜𝑔Δ𝜏𝑅)-(𝑙𝑜𝑔 𝑁) curves (S-N-curves), which correspond to typical detail categories. Each detail category is designated by a number which represents, in N/mm2, the reference value Δ𝜎𝐶 and Δ𝜏𝐶 for the fatigue strength at 2 million cycles.
How to select FAT class in SDC Verifier?
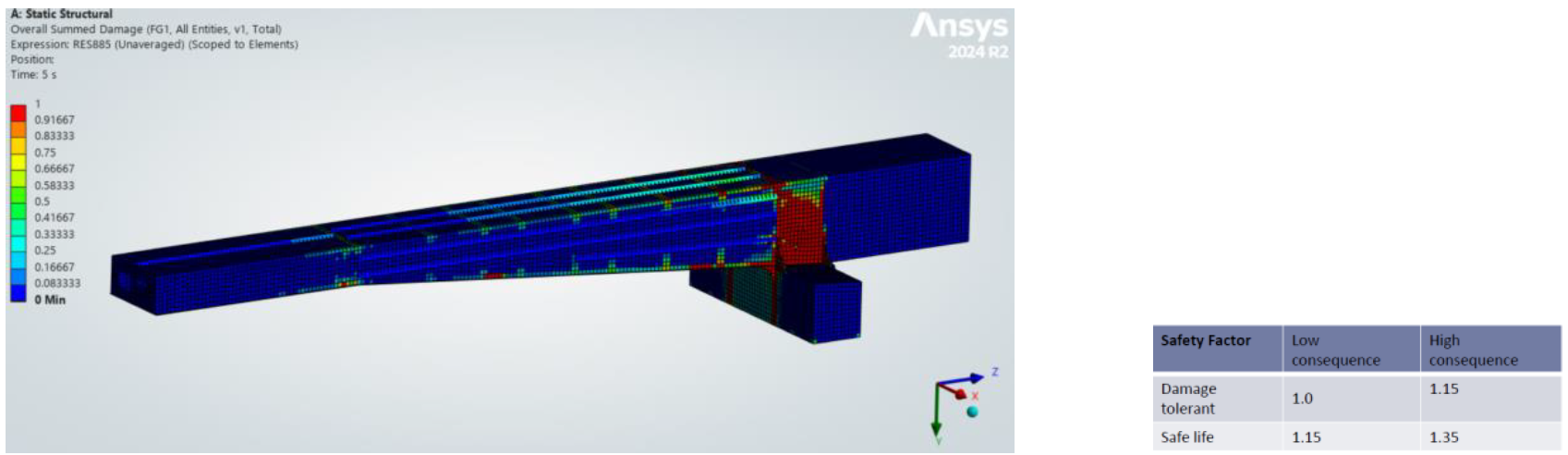
| Safety Factor | Low consequence | High consequence |
| Damage Tolerant | 1.0 | 1.15 |
| Safe Life | 1.15 | 1.35 |
Example
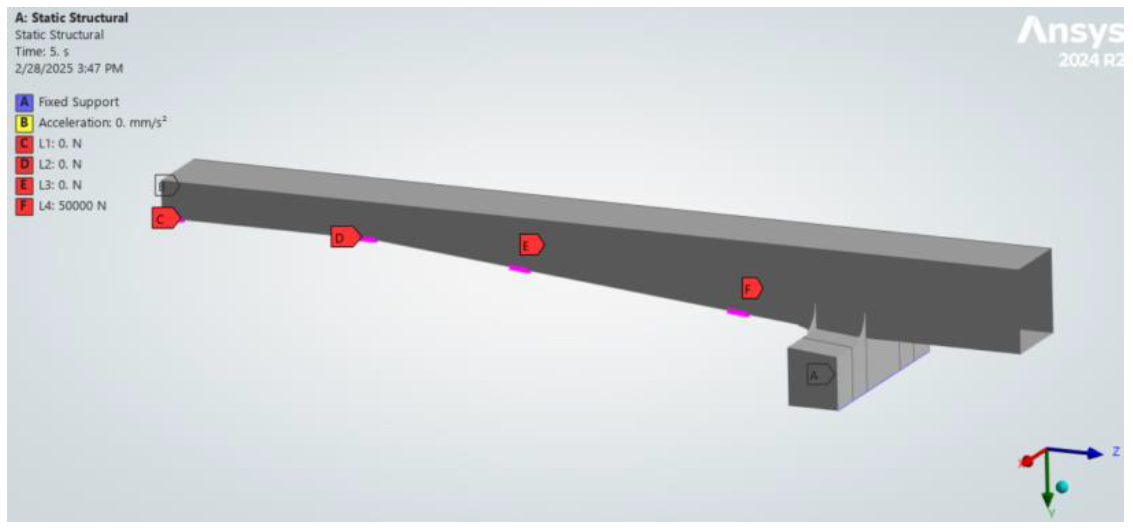
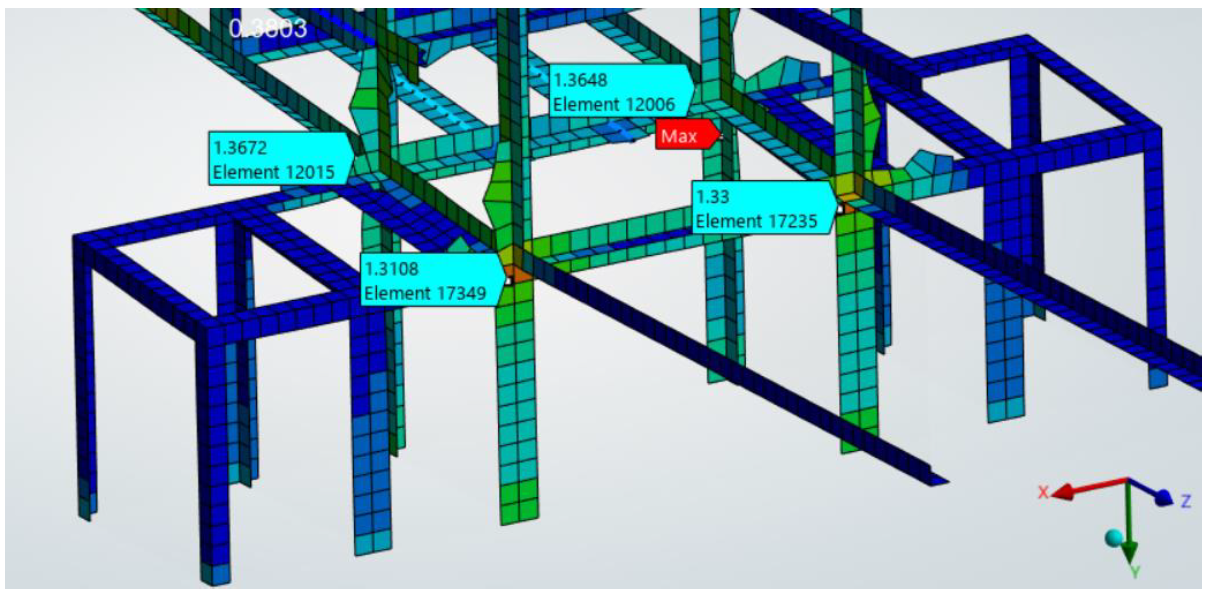
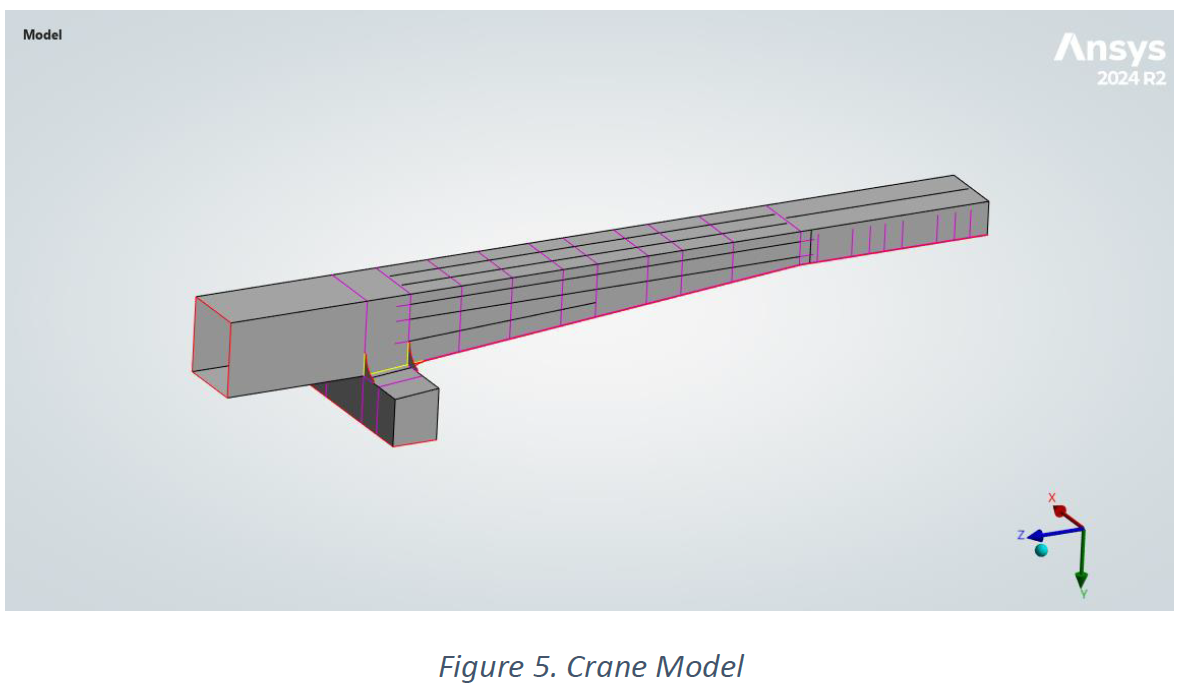
This crane model was subjected to mechanical loadings as shown below, and SDC Verifier was used to evaluate weld fatigue according to FEM 1.001 and Eurocode 3. The obtained results were then compared.
| Perpendicular to weld | Parallel with weld | Shear | |
| Weld | K1 | K2 | K0 |
| No Weld | W0 | 𝜏𝐷(-1) = 𝜎𝐷(-1) / sqrt(3) | |
| Steel Grade | 𝜎𝐷(-1) for κ=-1s element group 5 St 52-3 | |||||||
| Notch Group | W0 | W1 | W2 | K0 | K1 | K2 | K3 | K4 |
| Stress Amplitude | 163.8 | 130.3 | 104.2 | 118.8 | 106.1 | 89.1 | 63.6 | 38.2 |
Boundary conditions:
Results
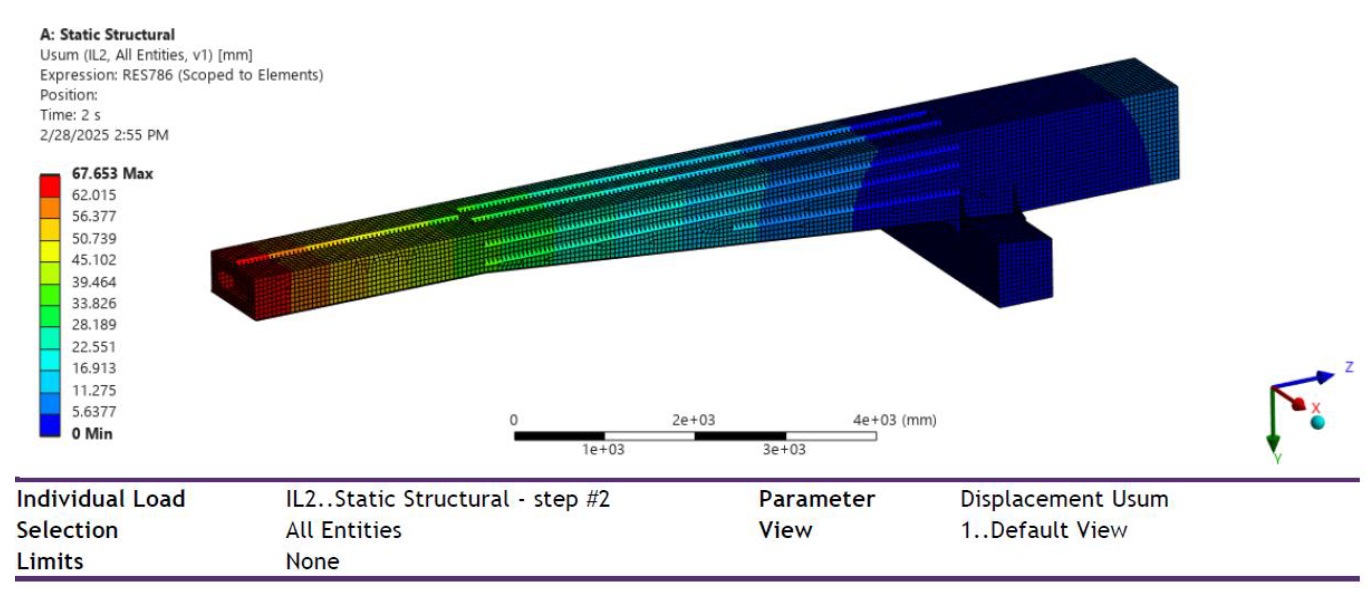
Max Displacement(mm):
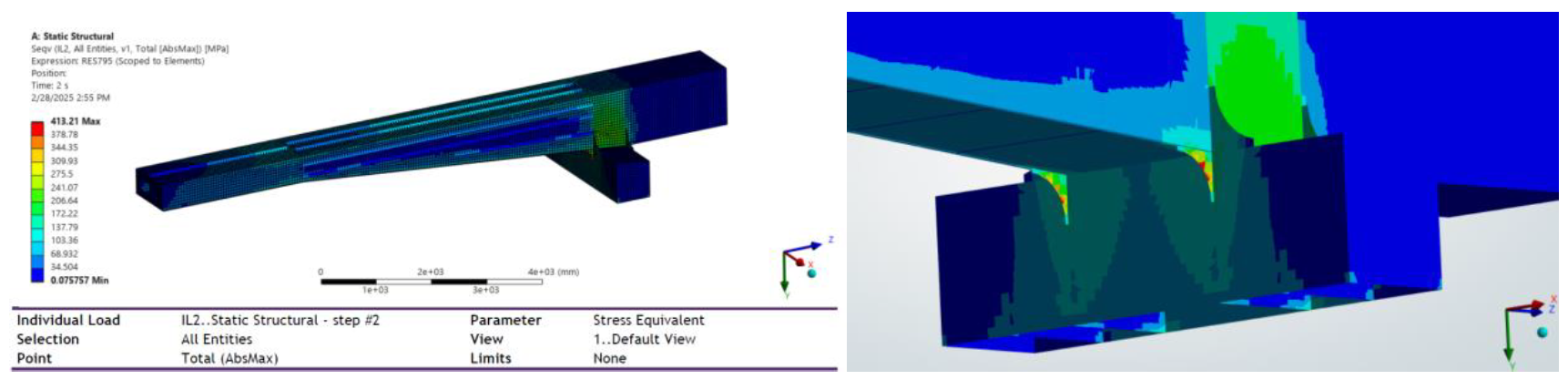
Max Stress(Mpa):
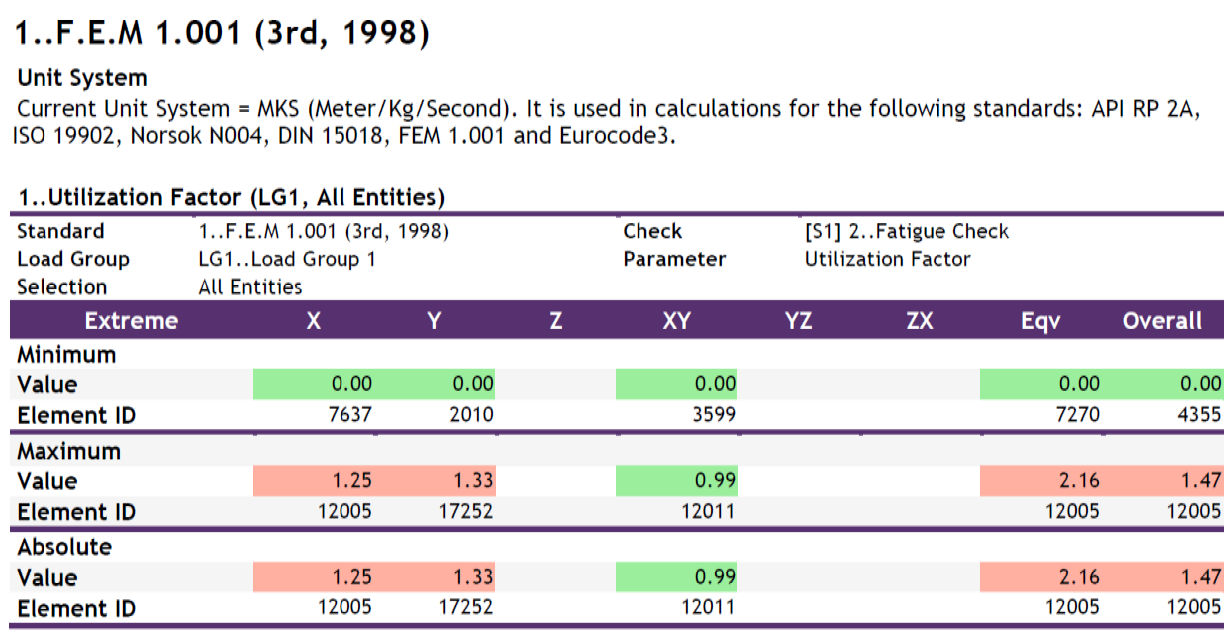
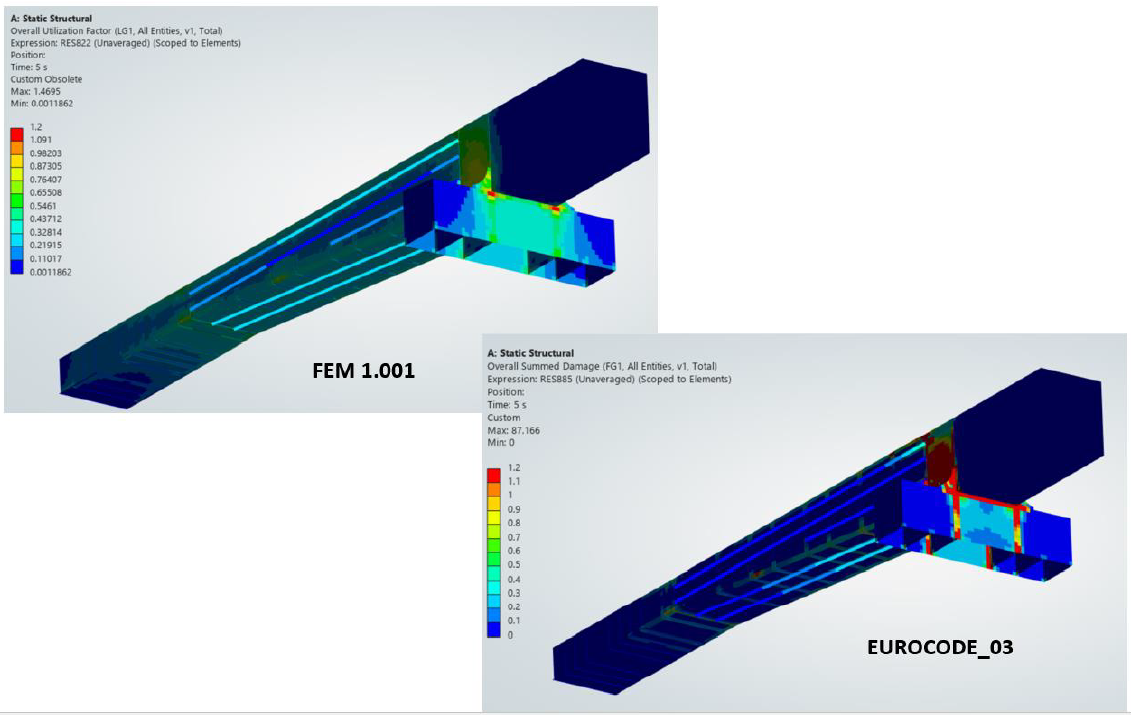
FEM 1.001 Utilization Factor Results
Table:
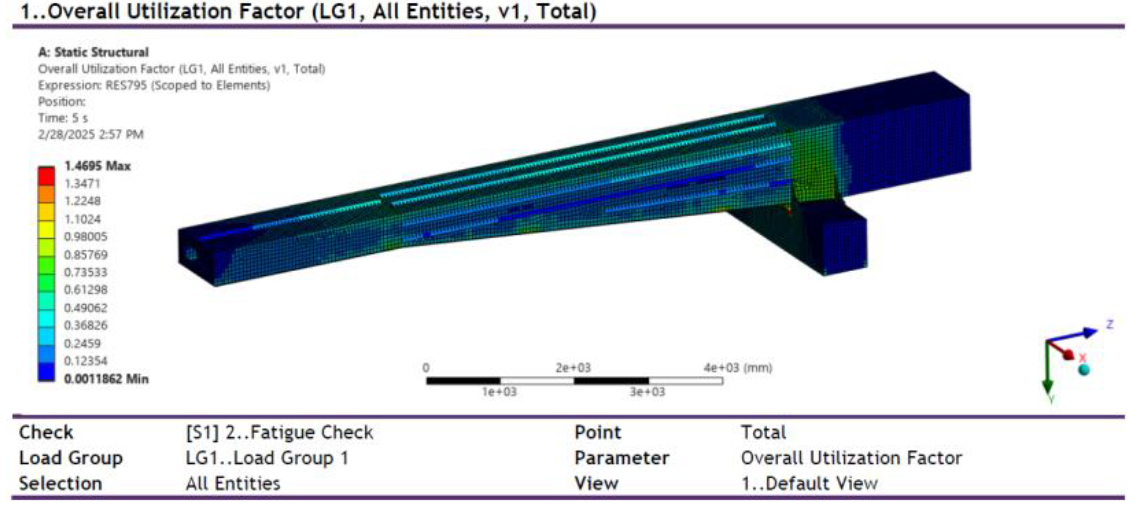
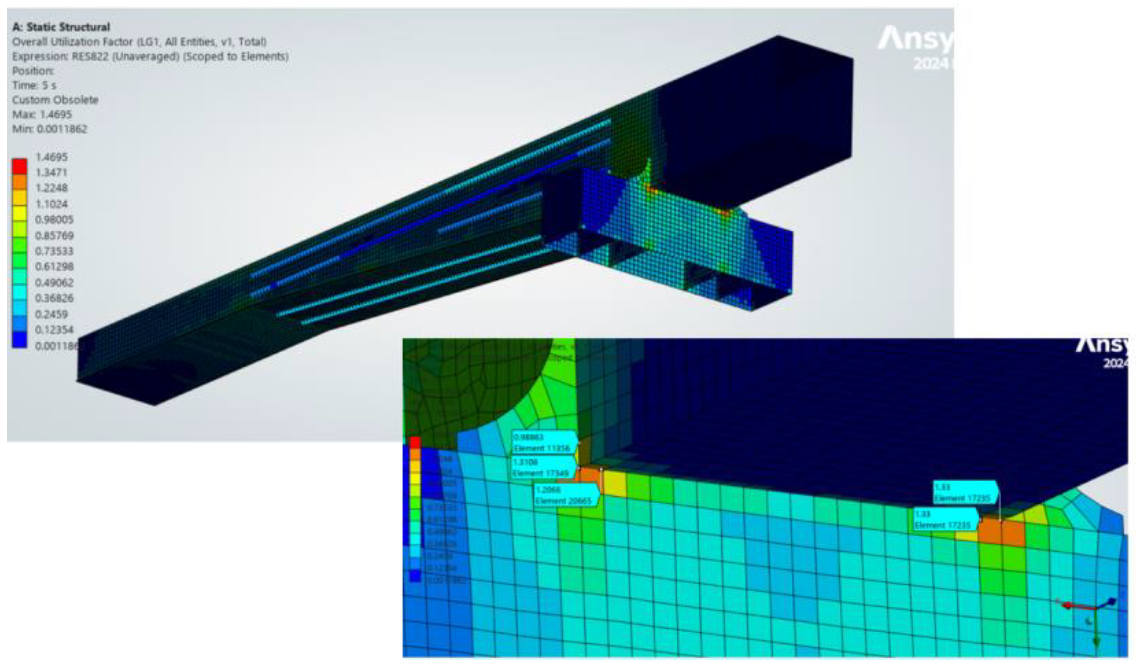
Plot (over All elements):
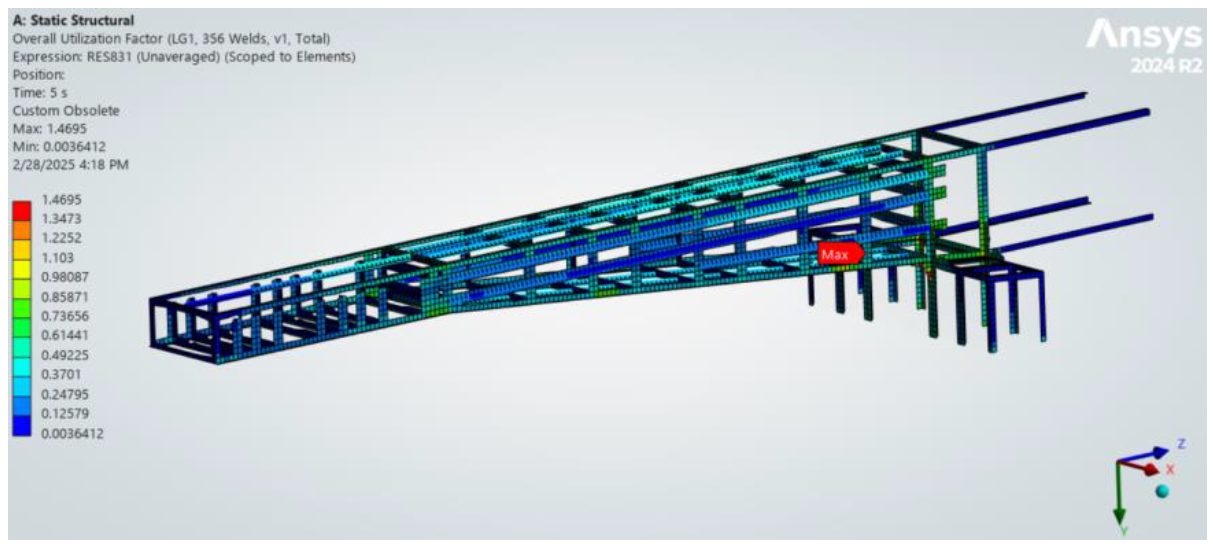
Plot (Over Weld Elements):
EUROCODE 03 Summed Dammage Results:
Conclusion
The study conducted by FE Tech highlights the differences between FEM 1.001 and Eurocode 3 in fatigue assessment. FEM 1.001 proves to be the superior choice for crane fatigue evaluation, offering more precise classifications and stress criteria. However, Eurocode 3 remains a valid option for general steel structures, where a more conservative approach is necessary.
By using SDC Verifier, engineers can seamlessly compare both standards, automating fatigue calculations and enhancing structural decision-making. Whether optimizing crane design or evaluating structural components, SDC Verifier provides a comprehensive toolset for fatigue verification.



 Identify the given κ value (x-axis).
Identify the given κ value (x-axis).