Why is it necessary for a civil engineer to know finite element analysis?

Civil engineering, a field dedicated to designing and constructing infrastructure, industrial and residential facilities, relies on advanced tools to ensure project safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Among these skills, Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a paramount skill for civil engineers. It revolutionized scientific modeling and engineering design, including water tanks, tunnels, underground and parking structures, bridges, highways, and high-rise buildings.
FEA Applications in Civil Engineering
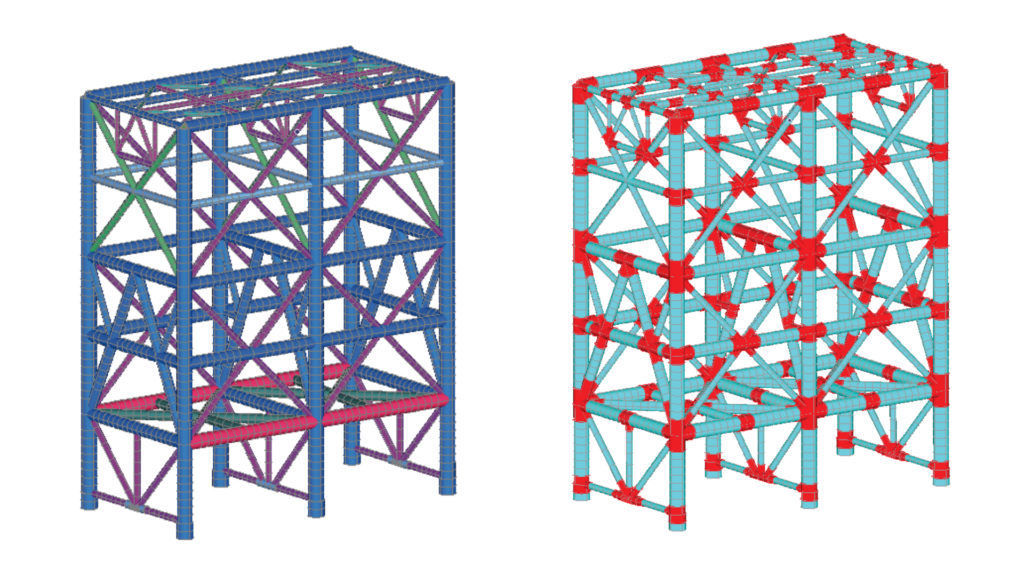
Finite Element Analysis is a powerful computational technique for analyzing complex structures, enabling civil engineers to simulate real-world conditions and predict how various factors impact the behavior of different materials. Applications extend to structural analysis, optimizing designs, predicting performance under diverse environmental conditions, and addressing challenges related to complex geometries.
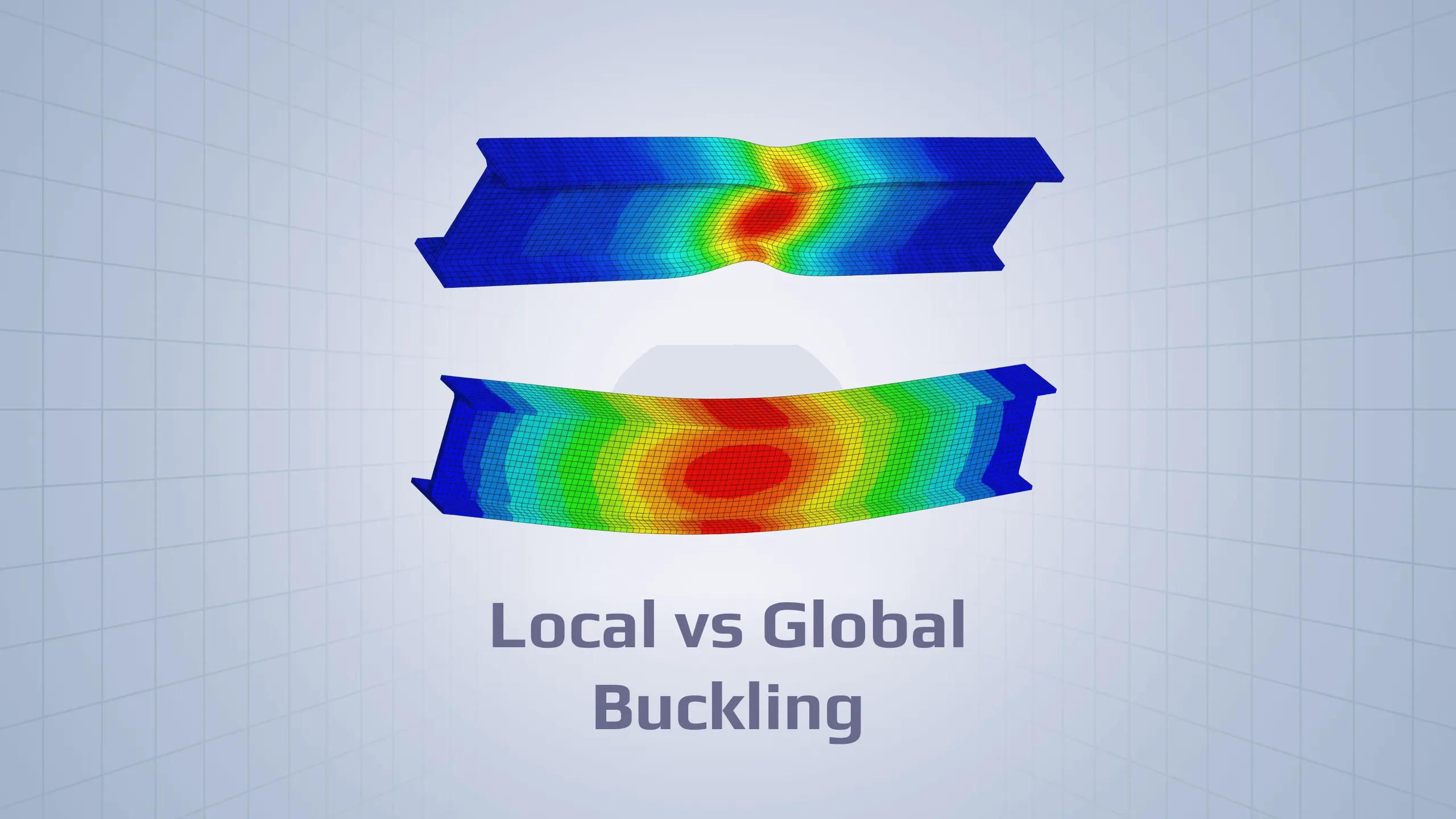
FEA becomes particularly crucial in seismic analysis, wind load assessments, complex beam connections, and other scenarios where traditional analytical methods may fall short. Its power comes from its ability to discretize a structure into a mesh of small elements, each governed by well-defined mathematical relationships. This makes it possible to simulate complex geometries, diverse material properties, and nonlinear behaviors that defy simple hand calculations.
Benefits of FEA in Civil Engineering
Finite Element Analysis has become an indispensable part of the structural engineer’s toolkit, transforming the way they design and analyze structures. Here are some of the key benefits of using FEA in civil engineering:
- Optimizing Designs: FEA allows civil engineers to iterate and optimize designs by simulating different configurations, materials, and dimensions, ensuring the most efficient and cost-effective solutions.
- Early Detection of Issues: Through FEA, potential failure points in a structure can be identified early in the design phase, enabling engineers to make informed decisions and prevent costly modifications during or after construction.
- Material Selection: FEA aids in selecting appropriate construction materials by simulating their behavior under various conditions, helping engineers choose materials that align with project requirements.
- Cost Savings: Simulating and analyzing structures before construction helps identify issues early, avoiding expensive modifications and ensuring projects stay within budget.
Enhancing Specialist Skills with FEA in SDC Verifier
Beyond its direct applications, proficiency in FEA enhances the skill set of civil engineers, offering several benefits:
- Specialized Expertise: Civil engineers with FEA skills possess technical expertise that is increasingly in demand, making them more competitive in the job market.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: FEA knowledge enables civil engineers to collaborate seamlessly with professionals from other disciplines, as the technique finds applications in geotechnical, environmental, and fluid dynamics analyses.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many engineering codes and standards mandate using FEA for specific projects. Mastery of FEA ensures that civil engineers meet these regulatory requirements, facilitating project approvals and compliance.
With SDC Verifier capabilities in structural analysis, design optimization, and failure prediction, civil engineers can streamline their workflow due to a user-friendly interface that enhances efficiency and reduces the learning curve. The advanced automatic reports generation feature ensures instant integration of any changes in input parameters into the design calculation report. Advanced capabilities allow engineers to import structural geometry directly from CAE software into SDC Verifier, saving significant time, or build a model from scratch by starting the design process with simulation first.
The constantly growing list of standards regulating Civil industry includes such rules as:
- AIJ-2017
- AISC ASD 1989
- AISC 360-10
- AISC 360-22
- AS 3990
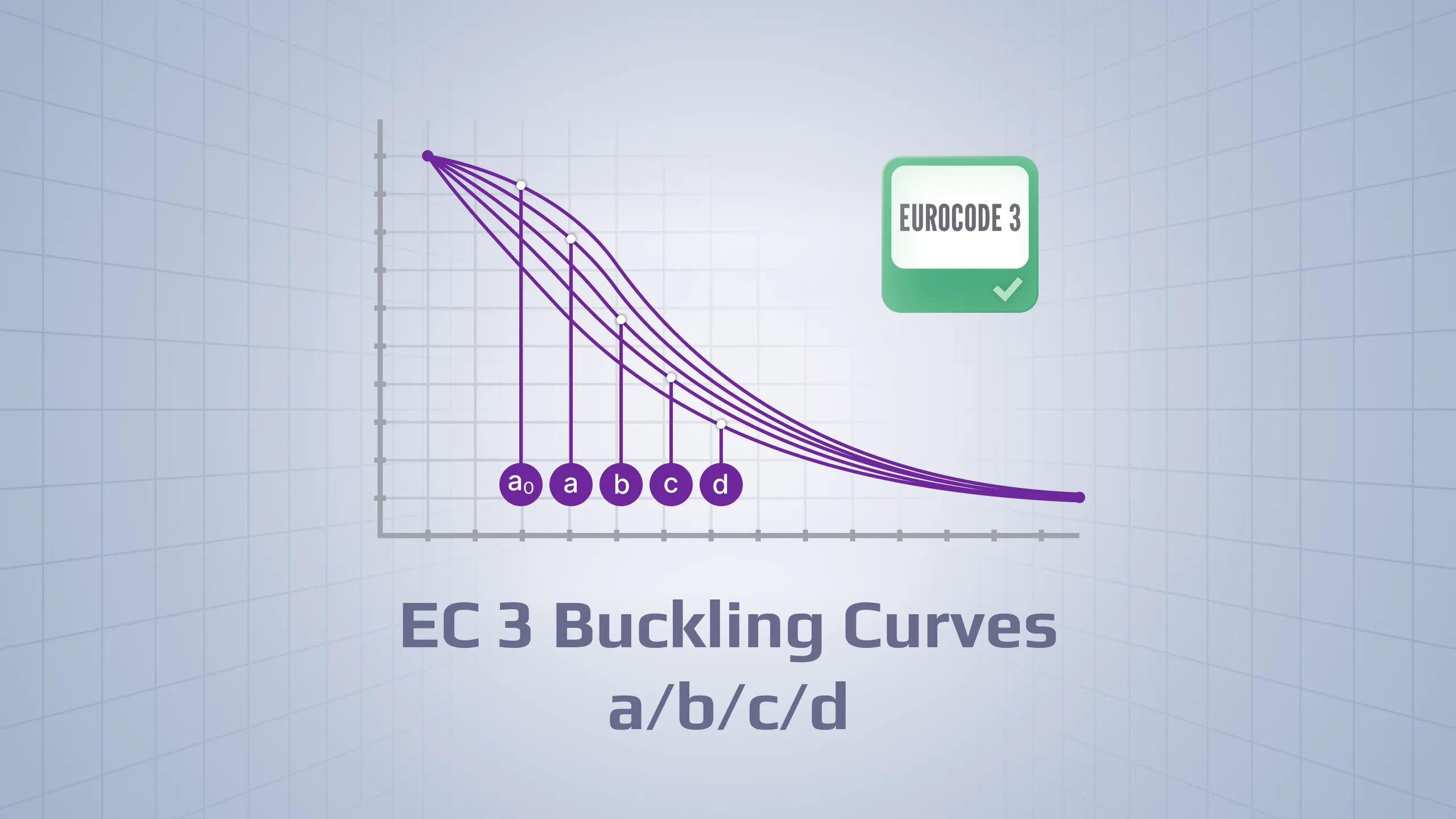
- Eurocode 3
- FEM 1.001
- FKM (5th and 6th editions)
- VDI 2230
Verification according to standards at any step of a structural engineering project helps to ensure compliance with all updated rules and regulations.
Conclusion
Finite Element Analysis enables civil engineers to build safe, durable, and cost-effective infrastructure through the use of simulation and analysis. This reduces the reliance on full-scale physical testing and helps accelerate design. It plays a critical role in ensuring the integrity and reliability of civil engineering projects.
The potential for using FEA in civil engineering is growing every year. And thanks to programs like SDC Verifier, with its flexible licensing policy and modular system, both large firms and freelance engineers can enjoy the benefits of using the finite element method in the civil engineering workflow.