How to Define Contact Regions in Structural Simulations?

In Finite Element Analysis (FEA), contact regions specify the areas on each body that may come into contact and define whether they are deformable or rigid. The actual interaction behavior is governed by the contact properties. Properly defining these regions ensures accurate simulations of stress distribution, deformation, and load transfer.
This article explores best practices for defining contact regions in FEA and explains how to apply them in SDC Verifier for structural verification.
See also our guide on contact conditions in FEA for key interaction types and their impact.
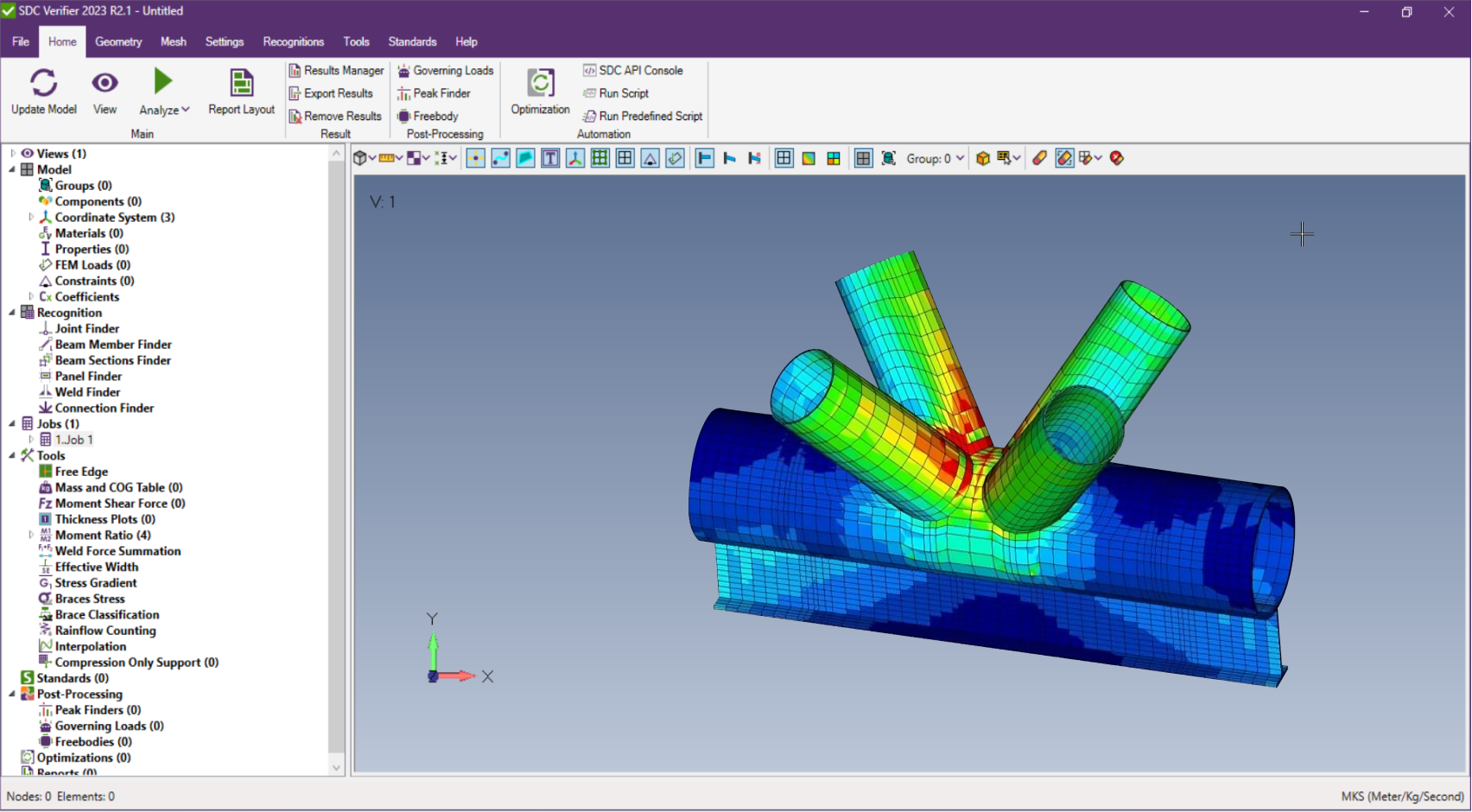
Defining Contact Regions in FEA
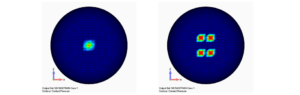
Contact regions define the areas on interacting bodies where physical contact may occur. Depending on the solver, these can be based on nodes, surfaces, or elements—without necessarily requiring separate contact elements.
Contact elements are specialized interface elements used to simulate areas where contact between components may occur. In SDC Verifier, contact can be defined using elements, nodes, or curves, with element faces specified for accurate interaction. These regions (or zones) are defined by two types of elements:
Target and source, which represent the active surface making contact, and which define the opposing surface. Also, you have to ensure that element normal direction is same for all elements in one region to avoid wrong results
Such regions determine how forces, friction, and constraints are applied in the simulation, preventing unrealistic material penetration and ensuring correct load transmission.

Types of Contact Regions
- Deformable Contact
- Allows relative motion and deformation of the interacting surfaces.
- Suitable for flexible components in mechanical assemblies.
- Rigid Contact
- Assumes one body remains completely stiff while the other conforms to its shape.
- Requires a Reference Node (Ref Node) for defining the rigid body behavior.
Applying Contact Regions in SDC Verifier
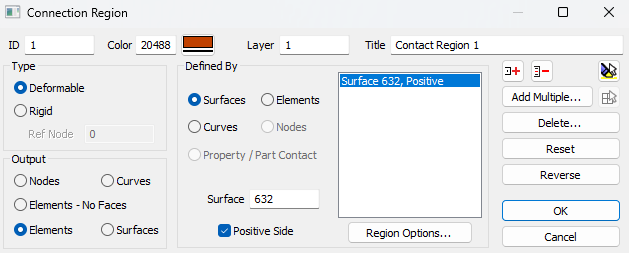
Creating a Contact Region
In structural analysis software like SDC Verifier, a contact region defines target and source part of contact interaction.
Follow these steps to create a contact region:
- Navigate to Model → Contacts → Contact Regions → Add.
- In the Add Contact Region window, configure the following settings:
- Type: Choose Deformable or Rigid.
- Ref Node (for Rigid Contact): Assign a reference node.
- Output: Select between Nodes, Elements No-Faces, or Elements.
- Defined By: Choose the relevant entity type (Elements, Nodes, Surfaces, Curves).
- Adjust the region’s visibility using Entity Visibility Control.
- Click Region Options to define an Offset Distance if required.
- Save the settings to add the contact region to the model and specify the face of the element which is in contact.
Importance of Proper Contact Regions in FEA
- Accurate Load Transfer – Contact regions ensure forces and stresses are correctly transmitted between interacting components, reflecting real-world conditions.
- Prevention of Unrealistic Behavior – Without proper contact definitions, parts may interpenetrate or separate unnaturally, leading to unrealistic simulations.
- Improved Convergence and Stability – Poorly defined contact conditions can cause solver instabilities and slow convergence. Well-defined contact improves computational efficiency and accuracy. Solver performance also depends on mesh quality and contact behavior.
- Realistic Stress Distribution – Proper contact modeling prevents artificially high stress concentrations or unrealistic deformations, ensuring the simulation reflects actual structural behavior.
By carefully defining contact regions, engineers can enhance the accuracy of their simulations, leading to better design decisions and improved structural performance.
Conclusion
Proper contact regions in FEA are crucial to ensure realistic load transfer, prevent unphysical penetration or gaps between interacting parts, and accurately simulate stress distribution. Poorly defined contacts can lead to incorrect results, such as excessive deformations or unrealistic stress concentrations. They also impact numerical stability, potentially causing convergence issues.
Properly modeling region is one of the most important contact settings and it may affect the whole behavior of contact in the model. In SDC Verifier, the Contact Regions tool provides an intuitive approach to defining and managing interactions, ensuring precise verification and compliance with engineering standards.